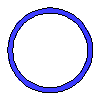
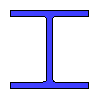
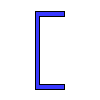
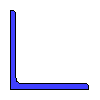
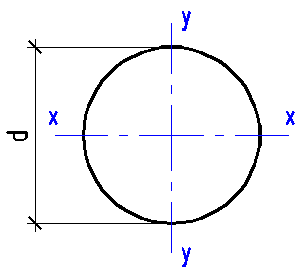
Data input:
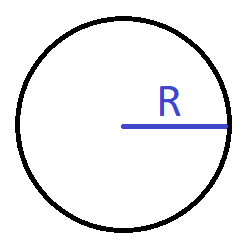
Diameter d
mm
| Name | Value | Units of Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Circle diameter | {{D1*k1_1 | fix2:x1}} |
|
| Circle area | {{A1*k1_2 | fix2:x2}} |
|
| Section modulus Wx | {{Wx1*k1_3 | fix2:x3}} |
|
| Section modulus Wy | {{Wy1*k1_4 | fix2:x4}} |
|
| Moment of inertia Ix | {{Ix1*k1_5 | fix2:x5}} |
|
| Moment of inertia Iy | {{Iy1*k1_6 | fix2:x6}} |
|
| Radius of gyration ix | {{ix1*k1_7 | fix2:x7}} |
|
| Radius of gyration iy | {{iy1*k1_8 | fix2:x8}} |
|
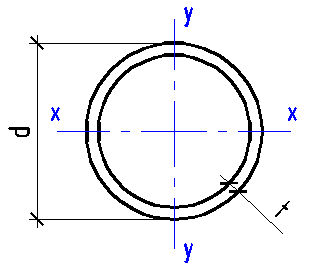
Data input:
Diameter d
mm
Wall thickness t
mm
| Name | Value | Units of Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Pipe diameter | {{D2*k2_1 | fix2:x9}} |
|
| Pipe area | {{A2*k2_2 | fix2:x10}} |
|
| Section modulus Wx | {{Wx2*k2_3 | fix2:x11}} |
|
| Section modulus Wy | {{Wy2*k2_4 | fix2:x12}} |
|
| Moment of inertia Ix | {{Ix2*k2_5 | fix2:x13}} |
|
| Moment of inertia Iy | {{Iy2*k2_6 | fix2:x14}} |
|
| Radius of gyration ix | {{ix2*k2_7 | fix2:x15}} |
|
| Radius of gyration iy | {{iy2*k2_8 | fix2:x16}} |
|
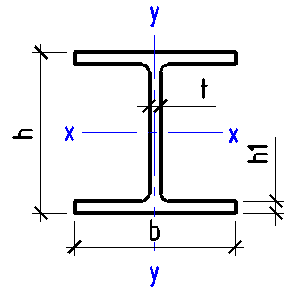
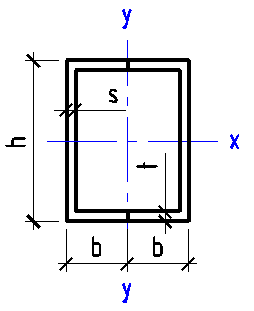
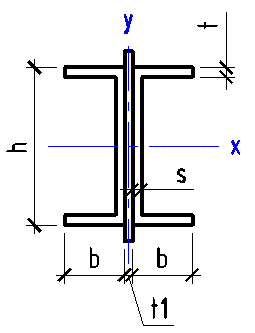
Data input:
Height h
mm
Width b
mm
Wall thickness t
mm
Flange height h1
mm
| Name | Value | Units of Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| I-beam area | {{A3*k3_2 | fix2:x17 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wx | {{ Wx3 *k3_3 | fix2:x18 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wy | {{ Wy3*k3_4 | fix2:x19 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Ix | {{ Ix3 *k3_5 | fix2:x20 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Iy | {{ Iy3*k3_6 | fix2:x21 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration ix | {{ ix3*k3_7 | fix2:x22 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration iy | {{ iy3*k3_8 | fix2:x23 }} |
|
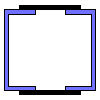
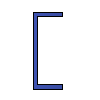
| Name | Value | Units of Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Channel area | {{ A4*k4_2 | fix2:x24 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wx | {{ Wx4*k4_3 | fix2:x25 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wy | {{ Wy4*k4_4 | fix2:x26 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Ix | {{ Ix4*k4_5 | fix2:x27 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Iy | {{ Iy4*k4_6 | fix2:x28 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration ix | {{ ix4*k4_7 | fix2:x29 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration iy | {{ iy4*k4_8 | fix2:x30 }} |
|
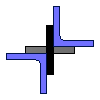
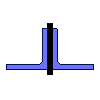

| Name | Value | Units of Measurement |
|---|---|---|
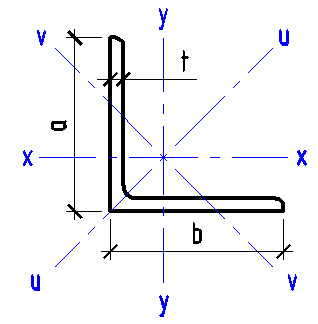
| Angle area | {{ A5*k5_2 | fix2:x31 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wx | {{ Wx5*k5_3 | fix2:x32 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wy | {{ Wy5*k5_4 | fix2:x33 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wuv | {{ Wuv5*k5_5 | fix2:x34 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Ix | {{ Ix5*k5_6 | fix2:x35 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Iy | {{ Iy5*k5_7 | fix2:x36 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Iuv (min) | {{ Iuv5*k5_8 | fix2:x37 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration ix | {{ ix5*k5_9 | fix2:x38 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration iy | {{ iy5*k5_10 | fix2:x39 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration iuv (min) | {{ iuv5*k5_11 | fix2:x40 }} |
|
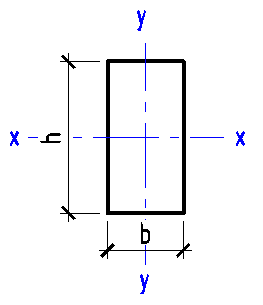
Data input:
Width b
mm
Height h
mm
| Name | Value | Units of Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle area | {{ A6*k6_2 | fix2:x41 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wx | {{ Wx6*k6_3 | fix2:x42 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wy | {{ Wy6*k6_4 | fix2:x43 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Ix | {{ Ix6*k6_5 | fix2:x44 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Iy | {{ Iy6*k6_6 | fix2:x45 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration ix | {{ ix6*k6_7 | fix2:x46 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration iy | {{ iy6*k6_8 | fix2:x47 }} |
|
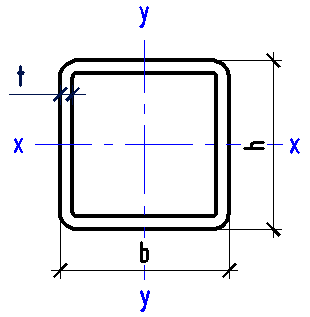
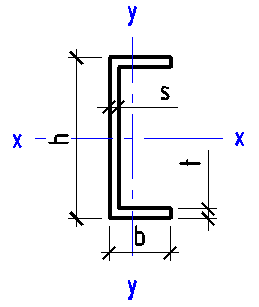
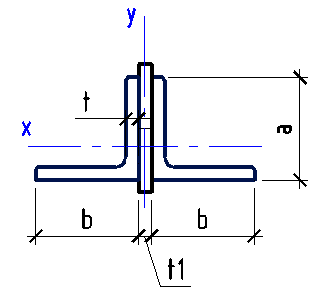
Data input:
Height h
mm
Width b
mm
Thickness t
mm
| Name | Value | Units of Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Pipe area | {{ A7*k7_2 | fix2:x48 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wx | {{ Wx7*k7_3 | fix2:x49 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wy | {{ Wy7*k7_4 | fix2:x50 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Ix | {{ Ix7*k7_5 | fix2:x51 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Iy | {{ Iy7*k7_6 | fix2:x52 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration ix | {{ ix7*k7_7 | fix2:x53 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration iy | {{ iy7*k7_8 | fix2:x54 }} |
|
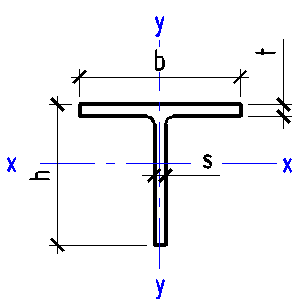
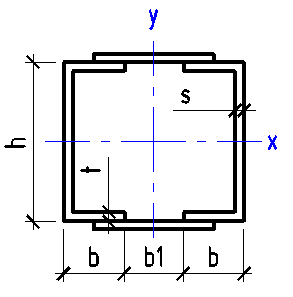
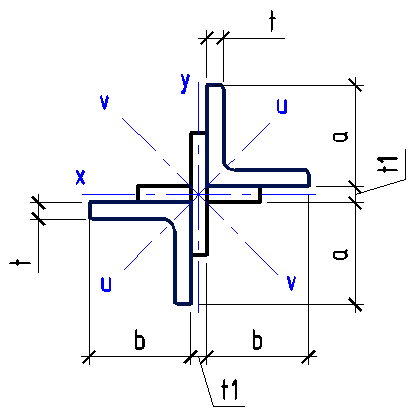
Data input:
Height h
mm
Width b
mm
Thickness t
mm
Thickness s
mm
| Name | Value | Units of Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| T-beam area | {{ A8*k8_2 | fix2:x55 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wx (top) | {{ Wx8*k8_3 | fix2:x56 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wx (bottom) | {{ Wx8_1*k8_9 | fix2:x62 }} |
|
| Section modulus Wy | {{ Wy8*k8_4 | fix2:x57 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Ix | {{ Ix8*k8_5 | fix2:x58 }} |
|
| Moment of inertia Iy | {{ Iy8*k8_6 | fix2:x59 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration ix | {{ ix8*k8_7 | fix2:x60 }} |
|
| Radius of gyration iy | {{ iy8*k8_8 | fix2:x61 }} |
|